Inverter is an electronic power converter which converts DC signal into AC signal. To understand this, let’s take an example. Your source of electric charge is battery connected to solar panel which provides DC power. You need to turn a light/fan on which requires AC signal for its operation. So you would need a device which could provide interface between the two. This interfacing device is called inverter which will convert DC signal of battery to AC signal which could run any of AC powered equipment at your home. Regular power inverters give square wave output. Here’s my guide to best 2000 watt inverter.
Read my guide on best solar fence charger here. Read my guide on best 3000 watt inverters here. Here’s the list of best 1000 watt inverter. Use free online inverter size calculator here.
What Does An Inverter Do
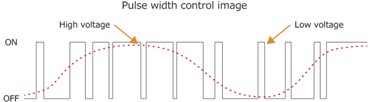
An inverter is primarily made of electronic switches. Switches that are controlled through software-based control systems. These switches are turned on and off to create a signal which oscillates between a fraction value of the DC input signal and ground creating a square wave based AC waveform.

As another option, switches are switched on and off in specific but complex manner such that width of resulting squared pulses is varied and controlled. These pulses create effect just like a smooth true sine wave when applied across terminals of an AC equipment.
Anyhow, some other electronic components (capacitor, ac inverter) can also be integrated into inverters to make smoother output signal.
Read why solar cells need inverter here.
Types of Power Inverter and Their Applications
Inverters can be categorized on the basis of input source, output waveform, number of phases or load type, modulation technique or number of output level. Here some of the important categorizations will be considered.
Read inverter vs. generator comparison here.
Power Inverter Input Source
- Voltage Source Inverter (VSI)
- Current Source Inverter (CSI)
Inverter input DC signal could be current or voltage making the inverter CSI or VSI respectively.
Voltage Source Inverter (VSI)
VSI has stiff voltage source at its input terminals to keep voltage magnitude constant. Stiff voltage source has zero impedance ideally. Practically, such source has very low impedance. This voltage source could be a battery connected to solar panel or a capacitor.
VSI inverters have capability to respond well to dynamic system events so they are widely used in modern Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS). VSIs are also used in UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) systems and motor control systems.
Read my comparison on NiCd Vs NiMh For Solar Lights here.
Current Source Inverter (CSI)
CSI has stiff current source at its input terminals so current magnitude doesn’t fluctuate with load variations. Stiff current source has high impedance. To keep the current constant at input terminals, either large inductor is used or a closed loop current controller is built.
CSIs are less popular as compared to VSIs because most appliances demand smooth sinusoidal voltage supply. Anyhow, these inverters are used in medium-voltage industrial applications where high quality current waveforms are needed.
Read my guide on Monocrystalline Vs Polycrystalline Solar Panels And Closest Competition.
Power Inverter Output Waveform
- Square Wave Inverter
- Sine Wave Inverter
- Modified Sine Wave Inverter
An inverter could yield square wave, or sine wave or modified sine wave.
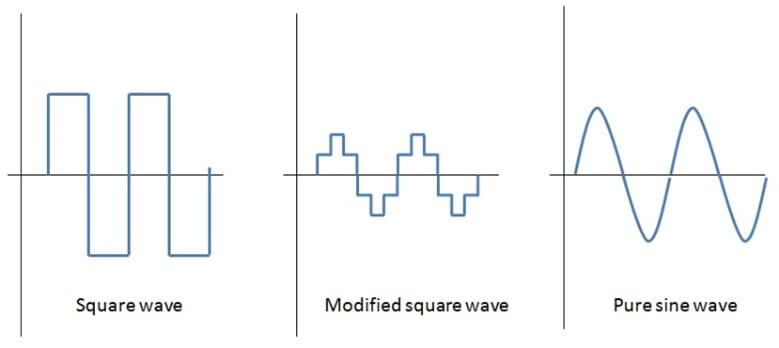
Square Wave Inverter
As indicated by name, Square wave inverter produces square wave at its output terminals. This type of inverter is simplest of all and very affordable. As most appliances are designed for sinusoidal waveform so square wave inverters are not used much. If square wave is applied to equipment needing sinusoidal signal, either it would be damaged or losses would be too high.
Read why china has the white house solar panels here.
Sine Wave Inverter
Pure sine inverter is common amongst all but complex to design. Ideally, these inverters give smooth sinusoidal waveform at their output terminals. Practically, there are little harmonic distortions in the wave which result in low-magnitude harmonics other than the required basic harmonic.
Pure sine wave inverters are used for almost all industrial, commercial and domestic applications.
- Kinverch 2000W pure sine wave power inverter,provide continuous DC to AC power and 4000W of peak power.featuring 3 AC outlets,1 USB port
Read Pros And Cons Of Solar Energy – Unbiased Facts And Comparison.
Modified Sine Wave Inverter / Quasi Sine wave Inverter
Output of square wave inverters switches abruptly between two values-maximum positive and maximum negative. On the other hand, sine wave inverters give output which is quite smooth and their value goes from one extreme to another without any abrupt change. Quasi sine wave inverters lie between these two. These inverters change their value from one peak to other in steps.
Such waveforms also have quite high content of harmonics and can damage appliance and cause noise during their operation.
- 2000 watts continuous power, 4000 watts peak power, KR2000 modified sine wave power inverter converts 12V DC to 120V AC power, connect DC battery cables directly to your 12V battery and you have power on the go
Read why Solar Tube Cost Is Important Here.
Power Inverter Load Type
- Single Phase Inverter
- Three Phase Inverter
For domestic applications, normally single phase supply is enough because load is small. For such loads single phase inverter suits much. For large commercial or industrial loads, three phase supply and thus three phase inverters are needed. So load type could also lead to categorization of inverters.
Single Phase Inverter
Single phase inverter takes DC input and gives one single AC output waveform. Single phase inverter could be half-bridge or full-bridge. Single phase half bridge inverter consists of two switches.
First switch is kept on for first half of the time period and second half for second half. Frequency of output waveform is controlled by changing switching frequency of electronic switches.
Read What Are The Advantages And Drawbacks To Solar Tube Lighting Here.

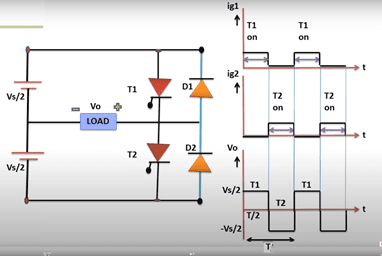
Here T1 and T2 are two thyristor switches and Vs is supply line DC voltage which is divided into two halves by combining two capacitors of same value in series.
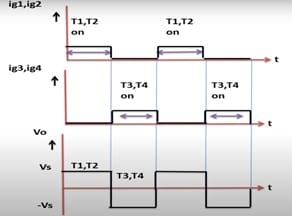
Single Phase Full Bridge Inverter has four switches and two of these conduct for one half cycle and other two, for the other half cycle.
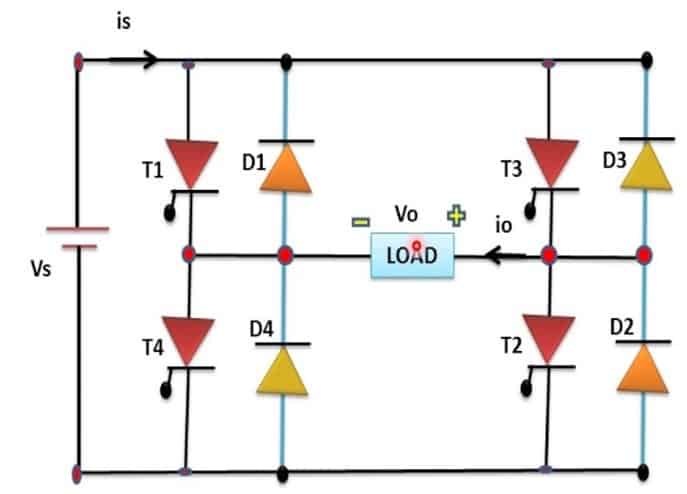
Diagram shows that thyristor T1 and T2 conduct for first half cycle and cause voltage drop across load to be positive. T3 and T4 conduct for second half cycle whereby voltage drop across load is negative.
Here’s everything you need to know about Solar Ready Electrical Panel.
Three Phase Inverter
Three phase inverter converts constant DC supply into three phase AC supply. Simple three phase inverters consist of three legs with each lag comprising of two switches. Output tapping is taken from the node point (common point) between two switches of a leg.
As three voltages of a three phase supply are displaced by 120 degrees from one another so switches are also controlled in such a manner that output waves from these three legs are 120 degrees from one another.
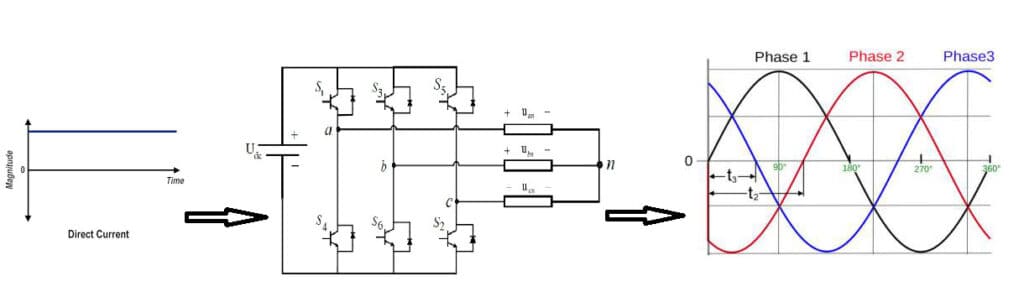
Diagram shows three phase inverter connected with a three phase balanced load. it is also shown how do output waveforms look alike when they are 120 degrees from one another.
These inverters are widely used in electric drives. It is key to emerging sustainable transportation technology. HVDC systems also need three phase inverters. Phase shifter inverters can shift single phase to three phase or vice versa. See details here.
Read How To Store Distilled Water – Number 6 Is The Cheapest.
Power Ratings Of Inverter
Inverter is rated in Watts (amps * volts). Usually, inverters come in ratings starting from few watts to thousands of watts (50-50,000 watts). For domestic applications, inverters rated below 11,000 watts are used often. Larger the load, larger the power rating of inverter is rule of thumb. Three type of ratings are studied for an inverter typically:
- Continuous Rating
- Surge Rating
- Short-term Rating
Continuous and Surge ratings are more important. Short-term rating is temperature/environment based and thus not mentioned usually. Mentioned rating is continuous rating normally. Manufacturer might or might not mention surge rating.
Applications and installed equipment directly influence the decision for selecting an inverter of some specific power rating. So it is essential to study startup and normal behavior of device before designing or installing inverter.
Read the Difference Between 12v And 24v Solar System.
Surge Rating
Some loads draw significantly heavy current on their startup like motors. Installed inverter needs to be rated such that it could provide that overload power without breakdown. Surge power might add 15-300% to continuous power. It usually lasts for 1-2 seconds or even less for inductive loads. Inverter manufacturers specify that this inverter can bear this surge power for these many seconds.
Read the differences of inverter vs. converter here.
Continuous Rating
After surge time is gone, devices keep on withdrawing some power continuously throughout their operating time. This continuous power specifies continuous rating. To calculate this rating for an inverter, power rating of all those devices is summed up which are to be connected to the inverter.
Here’s How To Get 12 Volts From A 24 Volt System – The Correct Method.
Difference Between AC And DC
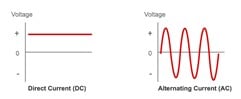
These days, we all use equipment which runs on electricity. Electric charge flow through such equipment is essential to make them work. This charge flow could be DC (Direct Current) or AC (Alternating Current). DC is the current which flows in one direction and its magnitude is constant provided there is no anomaly. AC current keeps changing its direction back and forth at regular intervals. These regular intervals determine frequency of AC current. For example, if some AC signal changes its direction 100 times in a second, then its frequency is 50 Hz.
Here is pictorial representation of AC and DC for understanding.
Solar Inverter
Solar inverter also called PV inverter converts variable DC electricity received from Photovoltaic cells to AC electricity which could be fed into commercial utility grid or utilized by home appliances.
Unlike traditional inverters, solar inverter also charges the battery from solar power and tends to switch to battery for DC supply when solar power is cutoff or below a benchmark value.
Read Advantages And Disadvantages Of Living Near A Solar Farm here.
Importance Of Solar Inverter
To contain rising global warming,, UN (United Nations) has set some Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Raising clean energy to reduce carbon footprint is one of these goals. Solar energy is one of the major sources for clean energy. Without solar inverters, solar energy has no place to go. So it can be said that solar inverters are integral part of solar systems.
Solar cells produce DC electricity which cannot be used by traditional electrical devices. Applying energy directly from solar cells to these devices could damage those devices so inverter interfacing between source and load is essential.
Moreover, solar inverters are considered the brain of solar system. They can detect if some of the cell or panel from amongst many is malfunctioning so it could be cutoff and others could make to work with maximum efficiency.
Here’s the Cost Of Solar Panels Per Square Meter. Use the best solar panel angle calculator here.
Power Inverter FAQ
Power inverters convert DC electricity to AC electricity and enable powering AC devices using DC power source. Inverter technology is evolving and we got Square Wave Inverter, Sine Wave Inverter, and Modified Sine Wave Inverter based on the output waveform. Inverter plays a crucial role in keeping our electrical appliances safer.
Read my guide on protecting solar panels from hail here. Read what makes inverter and generator different here.







